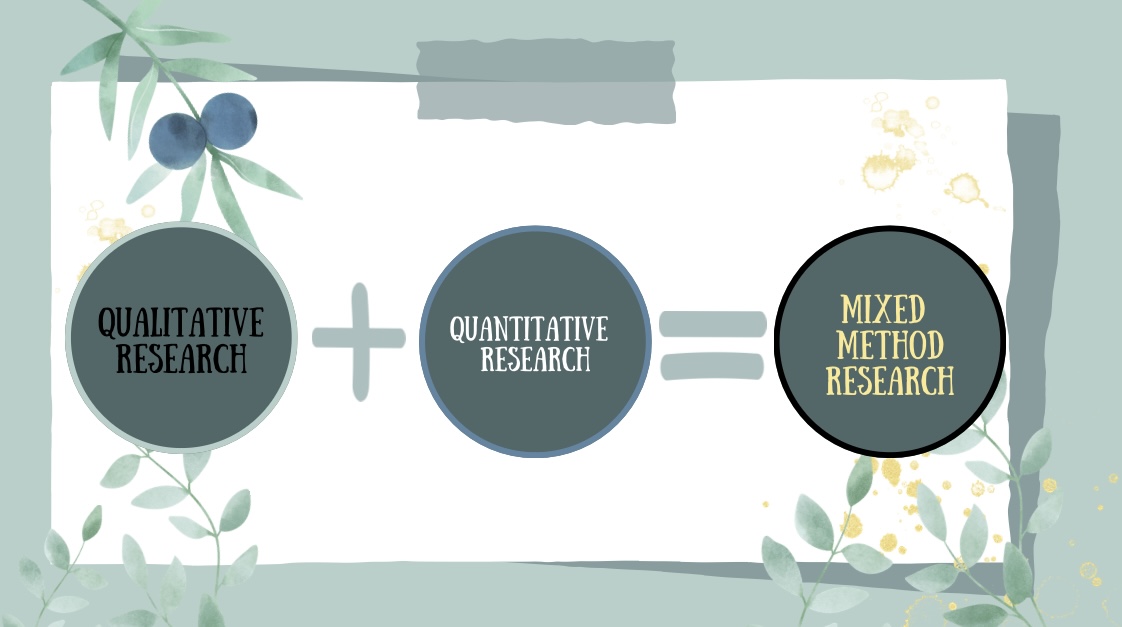
DEFINITION: mixed methods research combines elements of quantitative research and qualitative research order to answer your research question. Mixed methods can help you gain a more complete picture than a standalone quantitative or qualitative study, as it integrates benefits of both methods.
Mixed methods research may be the right choice if your research process suggests that quantitative or qualitative data alone will not sufficiently answer your research question.
CHARACTERISTICS:
1. The analysis of both qualitative and quantitative data.
2. The collection of both open and closed-ended data (qualitative and quantitative data) in response to research question.
3. Persuasive and rigorous procedures for the qualitative and quantitative methods.
4. The integration of these two data sources (by merging, connecting, embedding).
5. The use of specific mixed methods design that involves a concurrent or sequential integration.
MAIN USES:
ADVANTAGES:
1. Mixed methods research offers a richer and deeper data set that can capture the diversity and complexity of the research phenomenon.
2. It can enable the triangulation or corroboration of the data or results from different sources or methods, thus increasing the validity or trustworthiness of the research.
3. Mixed methods can allow for the exploration or explanation of the findings from one approach with the data or results from another approach, thus enhancing the interpretation or understanding of the research.
DISADVANTAGES:
Challenges can range from the need for more time, resources, skills, or expertise to plan, implement, and report the research, to ethical, practical, or theoretical issues related to the sampling, data collection, data analysis, or data integration.




.png)
Comments
Post a Comment